这篇文章的主要目标是验证光学相干断层扫描支气管镜(EB-OCT)在间质性肺疾病中的应用。作者还指出经支气管冷冻活检(TBLC)联合EB-OCT可能会提高诊断准确性,另外该技术的简单易学,临床医师能在短期培训后很快掌握。OCT成像技术适用于可弯曲支气管镜检查,它在肺部病变诊断上具有重要的作用和潜力。OCT具有的空间分辨率再现了支气管的剖面、外形,能获得高分辨率、横断面组织学的缩微图像,可以认为其光学活组织检查能够取代常规的切除活组织检查。它是一种高度可行的光学工具,实时检测并获得接近组织学成像的支气管内的病理学,在肺部疾病的监测、(鉴别)诊断和治疗上是很有潜力的。
(Nandy S, Raphaely RA, Muniappan A.etc. Diagnostic Accuracy of Endobronchial Optical Coherence Tomography for the Microscopic Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Nov 15;204(10):1164-1179. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202104-0847OC. PMID: 34375171)
原文摘要
Rationale: Early, accurate diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (ILD) informs prognosis and therapy, especially in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Current diagnostic methods are imperfect. HRCT resolution is limited while surgical lung biopsy (SLB) carries risks of morbidity/mortality.Endobronchial optical coherence tomography (EB-OCT) is a low-risk, bronchoscope-compatible modality that images large lung volumes in vivo with microscopic resolution, including subpleural lung, and has the potential to improve the diagnostic accuracy of bronchoscopy for ILD diagnosis.
背景:间质性肺病(ILD)的早期、准确诊断有助于预后和治疗,特别是特发性肺纤维化(IPF)。目前的诊断方法不完善。HRCT分辨率有限,而外科肺活检(SLB)具有死亡风险。支气管内光学相干断层扫描(EB-OCT)是一种低风险、与支气管镜兼容的成像方式,能够以显微镜分辨率显示较大体积肺,包括胸膜下肺,并有可能提高支气管镜诊断ILD的准确性。
Objectives: We performed a prospective diagnostic accuracy study of EB-OCT in ILD patients with a low-confidence diagnosis undergoing SLB. Primary endpoints were EB-OCT sensitivity/specificity for diagnosis of the histopathologic pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) and clinical IPF. The secondary endpoint was agreement between EB-OCT and SLB for diagnosis of the ILD fibrosis pattern.
目的:我们对接受 SLB 诊断的 ILD 患者进行了 EB-OCT 的前瞻性诊断准确性研究。主要终点是EB-OCT诊断病理表现为普通型间质性肺炎(UIP)和临床诊断IPF的敏感性/特异性。次要终点是EB-OCT和SLB诊断ILD纤维化模式的一致性。
Methods: EB-OCT was performed immediately prior to SLB. The resulting EB-OCT images and histopathology were interpreted independently by blinded, independent pathologists. Clinical diagnosis was obtained from the treating pulmonologists after SLB, blinded to EB-OCT.
方法:在 SLB 前立即进行 EB-OCT。由此产生的 EB-OCT 图像和组织病理学由盲法、独立的病理学家解释。临床诊断是从 SLB 后治疗的肺科医生处获得的,对 EB-OCT 不知情。
Measurements and Main Results: We enrolled 31 patients, and four were excluded due to inconclusive histopathology or lack of EB-OCT data. Twenty-seven patients were included in the analysis (16 men, average age: 65.0 years): twelve were diagnosed with UIP and fifteen with nonUIP ILD. Average forced vital capacity and DLCO were 75.3% (SD:18.5) and 53.5% (SD:16.4), respectively. Sensitivity and specificity of EB-OCT was 100% (95% CI: 75.8-100.0%) and 100% (79.6-100%), respectively, for both histopathologic UIP and clinical diagnosis of IPF. There was high agreement between EB-OCT and histopathology for diagnosis of ILD fibrosis pattern (weighted κ: 0.87, (0.72-1.0)).
测量和主要结果:我们纳入了31例患者,其中4例因组织病理学不确定或缺乏EB-OCT数据而被排除在外。分析中包括 27 名患者(16 名男性,平均年龄:65.0 岁):12 名被诊断为 UIP,15 名被诊断为非 UIP ILD。平均 FVC 和 Dl CO分别为 75.3% (SD, 18.5) 和 53.5% (SD, 16.4)。对于组织病理学表现为 UIP 的 IPF 的临床诊断,EB-OCT 的敏感性和特异性分别为 100%(95% 置信区间,75.8-100.0%)和 100%(79.6-100%)。EB-OCT 与组织病理学诊断 ILD 纤维化模式的一致性很高。
Conclusions: EB-OCT is a safe, accurate method for microscopic ILD diagnosis, as a complement to HRCT and alternative to SLB.
结论:EB-OCT 是一种安全、准确的微观的诊断ILD的方法,可作为高分辨率计CT扫描的补充和 SLB 的替代。
![图片[1]-支气管内光学相干断层扫描(EB-OCT)| 每周呼吸-每周呼吸](https://www.breathweekly.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/图1-5.png)
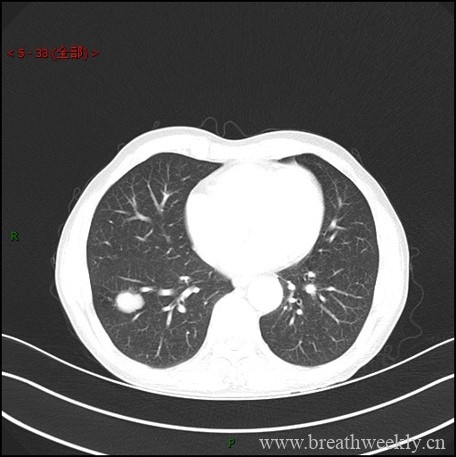
UIP类型的IPF的EB-OCT图像。(A)患者肺下叶EB-OCT和(B-C)相应横断面EB-OCT图像显示了UIP的特征。致密、信号强(浅灰色至白色)胸膜下纤维化(F) 已经破坏了肺泡结构。纤维化(F)内嵌有成簇增大、形状不规则、堆叠、信号差(黑色至深灰色)的囊性结构,与显微镜下观察一致蜂窝状(HC)。(D) 随后的SLB证实了致密的破坏性胸膜下纤维化(F),伴有罕见的单个囊性蜂窝状结构(HC)。
![图片[2]-支气管内光学相干断层扫描(EB-OCT)| 每周呼吸-每周呼吸](https://www.breathweekly.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/图2-6.png)
EB-OCT在临床ILD诊断工作流程中的潜在应用。HRCT:高分辨率CT;UIP:普通型间质性肺炎;IPF:特发性肺纤维化;ILD:间质性肺病;EB-OCT:支气管内光学相干断层扫描;TBLC:经支气管肺冷冻活检;SLB:外科肺活检。
欢迎搜索每周呼吸小程序和公众号,阅读文章病例更方便。
原文下载链接
[download id="3983"]






暂无评论内容